A new study has explored the dangerous effects smoking has on your body in the past and the present.
Researchers from the University of Leicester have taken a look at the impact smoking has on your bones in the long term, sharing images of just how damaging it can be.
In the UK alone, there were estimated to be 74,600 deaths attributable to smoking, the stats from 2019 suggest.
Advert
That number represented 15 percent of all deaths in 2019, according to the NHS.
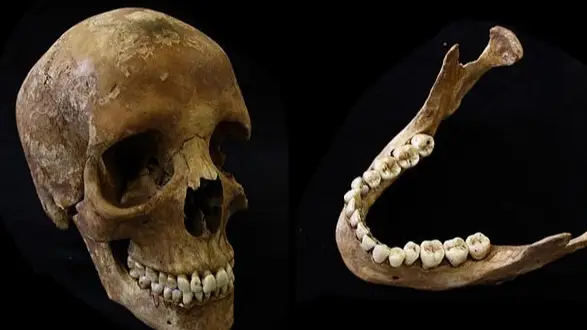
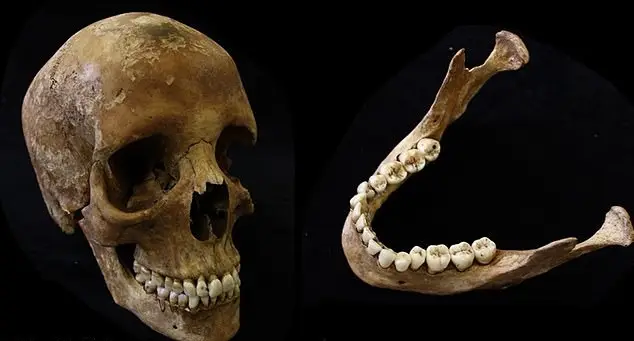
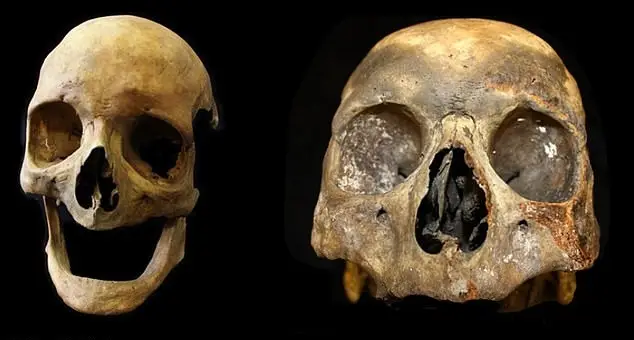
Now, the scientists decided to take a look at the remains of over a hundred people which were buried in England between AD 1150 and 1855.
This 'groundbreaking research' was basically done to 'understand health conditions in the past and their relationship to current trends'.
And this timeframe coincided with the arrival of tobacco in Western Europe in the 16th century.
The name Sir Walter Raleigh might ring a bell, as he's credited with bringing tobacco to England from Virginia on 27 July, 1586.
That being said, tobacco was also already being grown in England by the early 1570s.
Back to the study, the human remains showed that tobacco smoke left chemical molecules in the gnashers that could stay there forever.
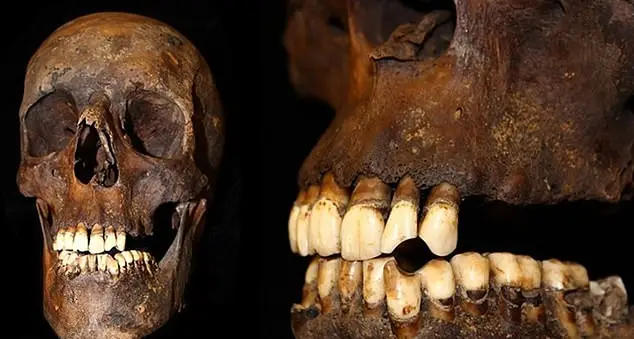
This is as well as staining and denting your teeth.
Lead author Dr Sarah Inskip explained: "Our research shows that there are significant differences in the molecular features contained in bone of past tobacco users and non-users.
"This potentially shows that we can see the impact that tobacco use has on the structure of our skeletons."
The researchers also noted: "Tobacco consumption affects human health, but no studies have investigated its effect on the bone metabolome, or if any changes are traceable after long postmortem intervals.
"Human osteoarchaeological remains preserve small molecules, making them valuable for studies that aim to examine past conditions.
"We test if there are molecular differences in the metabolome of cortical bone between archaeological individuals who used tobacco and those who did not, and if these differences are distinct enough to assign tobacco use status to individuals with unknown tobacco use.
"Tobacco consumption leaves a metabolic record in human bone distinctive enough to identify its use in individuals of unknown tobacco consumption.
"This groundbreaking research shows that archaeo-metabolomics has a lot to offer in terms of understanding past phenotypes, like tobacco smoking.
"[This] can help us better understand health conditions in the past and their relationship to current trends."
The study, titled Archaeometabolomics characterizes phenotypic differences in human cortical bone at a molecular level relating to tobacco use, can be read in full on Science Advances.