
Scientists were left perplexed after the discovery of the first ever 'hiccuping' black hole.
The cosmic beast was spotted by astronomers in a finding that has made scientists completely re-think theory on how black holes might behave.
It's a big old black hole too, weighing in at around 50 times mass of Earth's sun.

Advert
For those who aren't clued up, black holes are areas of such immense gravity that nothing, not even light, can escape from it.
Thankfully for humans, it's nowhere near our planet. In fact it's quite far away, at a staggering 800 million light-years from our planet.
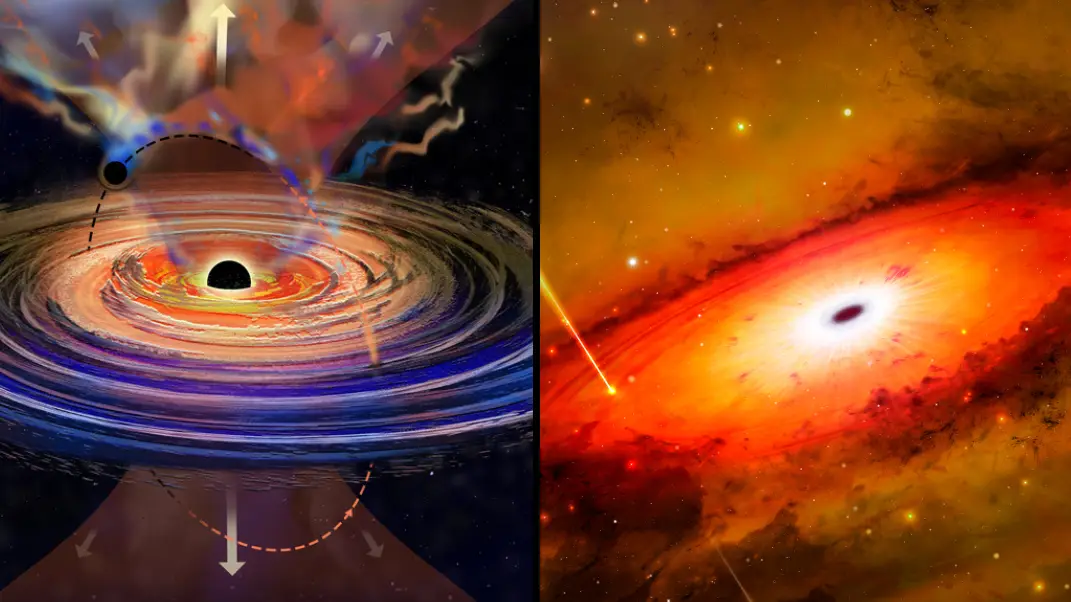
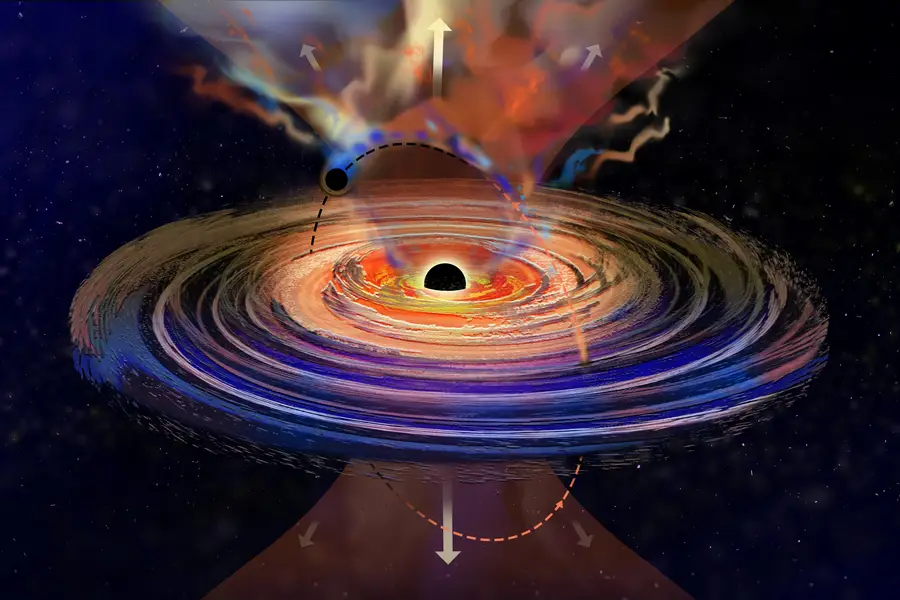
It is no ordinary black hole, with it being the first ever one to be spotted 'hiccuping' from its 'accretion disk'. This is the ring of extremely hot gas that swirls around the black hole itself.
The 'hiccuping' is where mass is being ejected form the supermassive black hole.
And now, a brand new study hints that the 'hiccuping' is happening due to yet another black hole that is orbiting its supermassive mate.
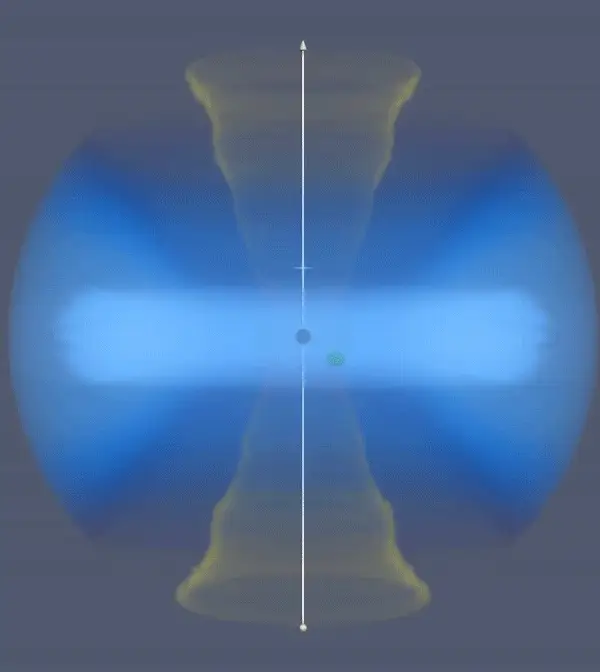
By orbiting around the larger black hole, the smaller one is kicking up a fuss and dragging matter away from the big beast.
It seems to happen every 8.5 days before going quiet until the next sequence.
Findings were published in a new study, published this month in the journal Science Advances.
Dheeraj Pasham, a scientist at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology's Kavli Institute for Astrophysics and Space Research, said: "This is a different beast. It doesn’t fit anything that we know about these systems. We thought we knew a lot about black holes, but this is telling us there are a lot more things they can do.
"We think there will be many more systems like this, and we just need to take more data to find them."
Speaking to Live Science, Pasham said the hiccups were a 'total surprise', adding: "We kept scratching our heads for months until the theorists in the Czech Republic came in and provided an explanation of a secondary black hole, which appears to explain all the properties of this system."
Researchers are of the opinion that the gravitational pull of the supermassive black hole will devour its younger and smaller neighbour.
They put this down to happen in more than 10,000 years time, though.

"This is a brilliant example of how to use the debris from a disrupted star to illuminate the interior of a galactic nucleus which would otherwise remain dark. It is akin to using fluorescent dye to find a leak in a pipe,” says Richard Saxton, an X-ray astronomer from the European Space Astronomy Centre (ESAC) in Madrid, Spain, who was not involved in the study.
“This result shows that very close super-massive black hole binaries could be common in galactic nuclei, which is a very exciting development for future gravitational wave detectors.”
Topics: Science, Space, Technology, Education, World News, NASA